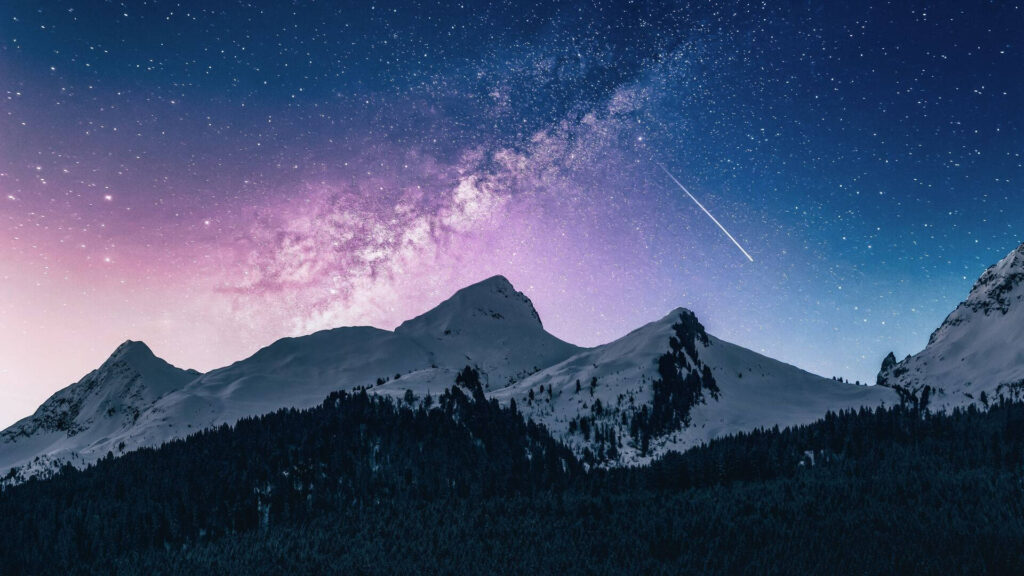
The words meteor, meteoroid, and meteorite are often confused. They describe the same object at different stages of its journey through space and into Earth’s atmosphere.
Meteoroids in Space
A meteoroid is a small natural object orbiting the Sun. These fragments usually come from asteroid breakups or dusty trails left by comets.
They can travel through the solar system for millions of years before approaching Earth.
What Is a Meteor
When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere at very high speed, the surrounding air heats up and glows, producing the visible streak called a meteor.
Bright meteors are sometimes called fireballs, while faint ones may last only a fraction of a second.
Meteor Showers
Meteor showers occur when Earth moves through dense streams of comet debris. Famous examples include the Perseids in August and the Geminids in December.
What Is a Meteorite
A meteorite is the solid fragment that survives atmospheric entry and reaches Earth’s surface.
Meteorites are grouped by composition:
- Stony
- Iron
- Stony iron
Scientists analyze these samples to determine their age and origin.
Classification and Study
Researchers examine mineral content, crystal structure, and isotopic signatures to trace meteorites back to specific asteroid families.
The Journey from Space to Earth
First, the object travels through space as a meteoroid.
Second, it creates light in the atmosphere as a meteor.
Third, any surviving pieces land as meteorites.
Why the Distinction Matters
Clear terminology helps scientists communicate accurately and allows the public to better understand astronomical events and potential impact risks.
Famous Impact Events
Earth bears many scars from past impacts, including the Chicxulub crater linked to the extinction of the dinosaurs. Smaller craters around the world also record ancient collisions.
Fun Facts
Scientists estimate that more than one hundred tons of small space debris enter Earth’s atmosphere every day, although most of it burns up before reaching the ground.
Understanding the difference between meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites reveals the full story behind a shooting star. These visitors from space provide insight into the origins and ongoing activity of our solar system.