1. What Is an Iron Plate?
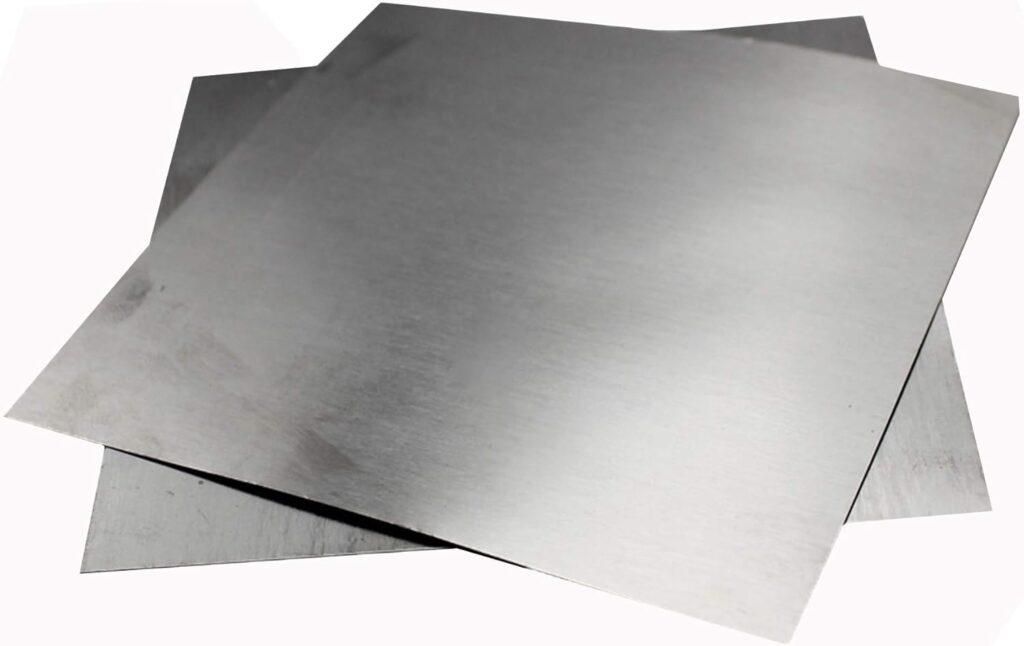
An iron plate, also known as a steel plate, is a flat sheet of iron or steel produced through rolling processes.
It serves as a fundamental material in various industries including construction, manufacturing, automotive, and shipbuilding because of its strength, durability, and versatility.
Iron plates come in different thicknesses, sizes, and grades, depending on their intended use. They can be cut, welded, and shaped easily, making them suitable for both structural and fabrication purposes.
2. Common Types of Iron Plates
Different types of iron plates are designed to meet specific structural and industrial needs.
Here are the most commonly used ones:
- Mild Steel Plate (MS Plate)
- Made from low-carbon steel.
- Easy to weld and shape.
- Ideal for general fabrication and construction projects.
- Checkered Plate (Tear Drop Plate)
- Features raised patterns on the surface to prevent slipping.
- Commonly used for flooring, stair treads, and walkways.
- Galvanized Iron Plate (GI Plate)
- Coated with zinc to protect against rust and corrosion.
- Suitable for roofing, outdoor applications, and marine use.
- Carbon Steel Plate
- Contains higher carbon content for improved strength and hardness.
- Used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
- Stainless Steel Plate
- Highly resistant to corrosion and heat.
- Often used in food processing, chemical, and medical industries.
- Hot Rolled Plate vs. Cold Rolled Plate
- Hot Rolled: Processed at high temperatures; has a rough surface but strong structure.
- Cold Rolled: Processed at room temperature; smoother and more precise dimensions.
ALSO SEE : Pencil – The Simple Tool That Shapes Ideas
3. Uses of Iron Plates
Iron plates are incredibly versatile and used in countless applications across multiple industries:
- Construction: Beams, floors, columns, and reinforcement plates.
- Shipbuilding: Hulls, decks, and marine platforms.
- Automotive: Chassis, panels, and truck bodies.
- Manufacturing: Machine parts, tanks, and tools.
- Infrastructure: Bridges, pipelines, and railway systems.
- Decorative Metalwork: Gates, signage, and furniture.
4. Advantages of Using Iron Plates
Choosing iron plates offers several benefits that make them a top choice in modern industries:
High Strength and Durability – Ideal for heavy-duty structures and long-lasting projects.
Corrosion Resistance – Especially when galvanized or stainless steel versions are used.
Easy to Fabricate – Can be cut, welded, or bent into different shapes.
Cost-Effective – Affordable and readily available in various grades.
Wide Range of Applications – Suitable for both industrial and aesthetic purposes.
5. How to Choose the Right Iron Plate
To ensure you get the best quality for your project, keep these factors in mind:
- Determine the Required Thickness – Thicker plates provide more strength and stability.
- Select the Right Material Type – Choose mild, galvanized, or stainless steel based on your environment.
- Inspect Surface Quality – Avoid plates with cracks, rust, or uneven surfaces.
- Check Certifications – Ensure compliance with standards like ASTM, JIS, or SNI.
- Buy from Reliable Suppliers – Trusted vendors guarantee consistency and quality.
6. Conclusion
The iron plate is one of the most essential materials in both industrial and construction sectors.
Its combination of strength, adaptability, and cost efficiency makes it a go-to choice for engineers, builders, and manufacturers worldwide.
Whether you’re building a bridge, fabricating machinery, or creating custom metalwork, iron plates deliver reliability and performance every time.
ALSO SEE : Explore Stonehenge, England: The Mysterious Megalithic Monument