Sound is one of the most fascinating phenomena in the natural world. Known as “suara” in Indonesian, sound is more than just what we hear; it has unique properties that make it essential in science, nature, and technology. From invisible vibrations to natural acoustic marvels, exploring the uniqueness of sound reveals its mysterious and practical roles in our lives.
1. Sound Travels at Different Speeds
Sound moves at different speeds depending on the medium:
- Air: ~343 m/s
- Water: ~1,480 m/s
- Steel: ~5,960 m/s
This explains why you can hear echoes differently or feel vibrations through walls and floors.
2. Ultrasound and Infrasound
Sound exists beyond human hearing:
- Ultrasound (>20,000 Hz): Used in medical imaging, cleaning, and dog whistles.
- Infrasound (<20 Hz): Can be felt rather than heard; used by elephants and whales for communication and by scientists to monitor volcanic eruptions or earthquakes.
These extremes of frequency highlight the hidden spectrum of sound.
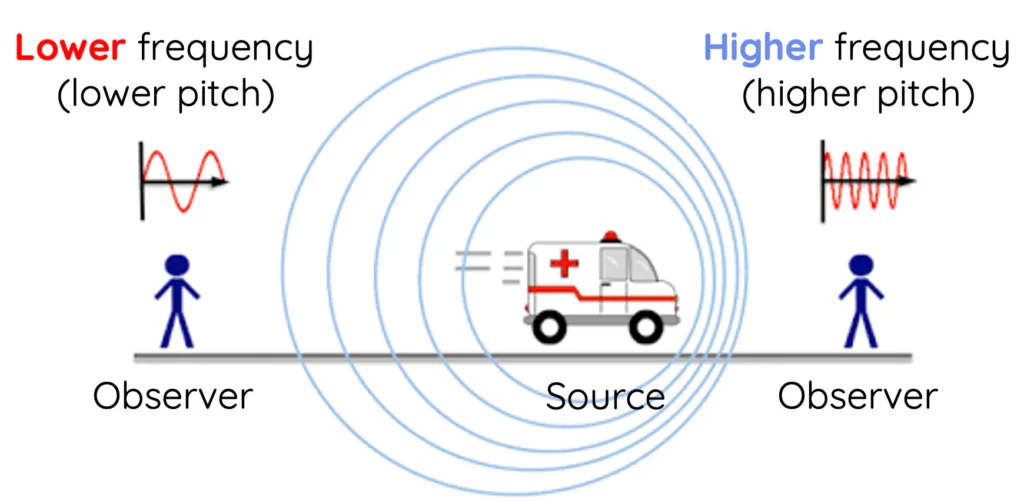
3. The Doppler Effect
The Doppler Effect occurs when the source of a sound moves relative to the listener, changing the perceived pitch:
- Example: An approaching ambulance siren sounds higher, then lower as it passes.
- Applications: Radar, astronomy, and medical imaging.
This effect is a unique aspect of sound that connects physics with everyday life.
4. Resonance: Natural Amplification of Sound
Every object has a natural frequency. When sound matches this frequency, it can resonate and amplify:
- Example: Opera singers breaking a glass with their voice
- Example: Musical instruments producing clear, powerful tones
Resonance demonstrates the magical interplay between physics and music.
5. Unique Sound Phenomena in Nature
Nature creates some of the most extraordinary sounds:
- Singing sands: Deserts produce a humming sound when sand shifts.
- Whale songs: Travel hundreds of miles underwater.
- Elephant infrasound: Enables communication over long distances.
These examples show that sound is not limited to humans but is a universal natural phenomenon.
Key Facts About Sound
- Sound: Vibrations traveling through a medium.
- Frequency: Determines pitch, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Amplitude: Determines loudness.
- Unique aspects: Doppler Effect, ultrasound, infrasound, resonance, and natural acoustic phenomena.
Conclusion
Sound is far more than just a simple vibration. Its unique properties—from extreme frequencies to natural resonance demonstrate its power and versatility. By exploring these facts, we gain insight into nature, technology, and the art of listening.