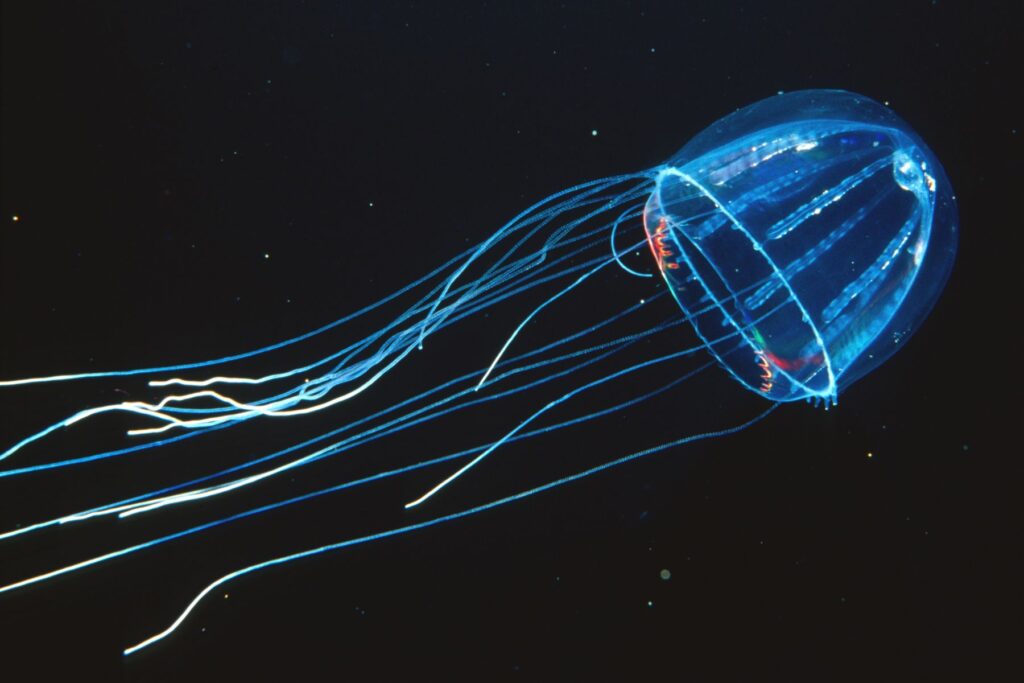
Bioluminescence is one of the most fascinating natural phenomena on Earth. It refers to the ability of living organisms to produce light through chemical reactions inside their bodies. While many people associate glowing creatures only with fireflies, the truth is that bioluminescence exists across a wide variety of species, both on land and in the deep ocean. This extraordinary natural process has inspired scientific research, cultural stories, and technological innovation. For many travelers and nature lovers, seeing bioluminescence in person becomes a once in a lifetime experience.
What Is Bioluminescence and How Does It Work
Bioluminescence is created when a molecule called luciferin reacts with oxygen, usually with the help of an enzyme known as luciferase. This reaction releases energy in the form of light. While the scientific process sounds simple, the way each species controls and uses that light can be incredibly complex. Some organisms flash their light to communicate, while others emit a steady glow to attract prey or deter predators.
Interestingly, bioluminescent light is often blue or green because these colors travel farther in water. This is why deep sea environments are dominated by bluish light rather than other colors of the spectrum.
Bioluminescence in the Deep Ocean
Most bioluminescent organisms live in the ocean, especially in deep environments where sunlight cannot penetrate. In these dark zones, bioluminescence plays essential roles in survival.
Deep sea fish such as the anglerfish use a glowing lure to attract prey. Jellyfish create light as a defensive mechanism, confusing predators in the darkness. Some species of squid release glowing clouds to distract attackers while they escape.
Scientists estimate that more than 75 percent of marine animals in the deep sea can produce light. This makes the deep ocean one of the brightest natural environments on Earth in terms of biological light, even though it appears pitch black to the human eye.
Glow in the Night on Land
Although less common, bioluminescence also exists on land. Fireflies are the most famous example. They use blinking patterns to communicate with potential mates. Each species of firefly has its own unique rhythm, allowing them to identify one another easily.
Fungi also display bioluminescence. Known as foxfire or fairy fire, glowing mushrooms can be found in various forests around the world. These mushrooms emit a soft green glow that has inspired myths and folklore for centuries.
Another land based example is the New Zealand glowworm. These creatures illuminate the inside of caves with bright blue dots, creating a starry sky like effect underground. Tourists from around the world travel to places like the Waitomo Glowworm Caves to witness this mesmerizing natural light show.
Bioluminescence Tourism Around the World
In recent years bioluminescence tourism has become increasingly popular. Travelers seek destinations where plankton or algae create glowing waves at night. When these microorganisms are disturbed by movement, they emit a bright blue light, creating shimmering trails in the water.
Some of the most famous bioluminescence destinations include:
- Mosquito Bay, Puerto Rico
Considered one of the brightest bioluminescent bays in the world, this location attracts thousands of visitors each year. - Toyama Bay, Japan
During certain seasons, glowing firefly squid gather near the shore, creating an unforgettable neon blue spectacle. - Maldives
Beaches in the Maldives often experience natural blue waves caused by bioluminescent plankton, giving travelers the impression of stars washing up on the sand.
These natural attractions highlight the beauty of bioluminescence and help raise awareness about ocean conservation.
How Bioluminescence Inspires Modern Technology
Beyond its visual beauty, bioluminescence is a growing area of scientific interest. Researchers are exploring how bioluminescent systems might be used in fields such as medical imaging, environmental monitoring, and energy efficient lighting.
Some scientists are developing bioluminescent plants that glow softly at night without using electricity. Others study glowing proteins to understand disease processes inside human cells. Bioluminescent markers allow doctors and researchers to track the behavior of specific genes or monitor the effectiveness of treatments in real time.
These innovations show how nature can lead to new sustainable technologies and scientific breakthroughs.
The Future of Bioluminescence Research
As technology improves, the study of bioluminescence continues to expand. Deep sea exploration with advanced submersibles allows scientists to discover new glowing species regularly. Genetic research provides insight into how organisms developed this ability over millions of years.
Bioluminescence not only helps us understand marine ecosystems but also inspires new creative ideas in storytelling, art, and design. From glowing animals in movies to bioluminescent themed installations in museums, this natural phenomenon continues to spark human imagination.
Bioluminescence is a remarkable example of nature’s creativity. Whether in the ocean, in a forest, or inside hidden caves, glowing organisms remind us of the planet’s beauty and mystery. As science uncovers more about this natural light, humans gain both knowledge and inspiration. For anyone who loves exploring unique natural wonders, witnessing bioluminescence in person can become an unforgettable experience that connects them deeply with the natural world.