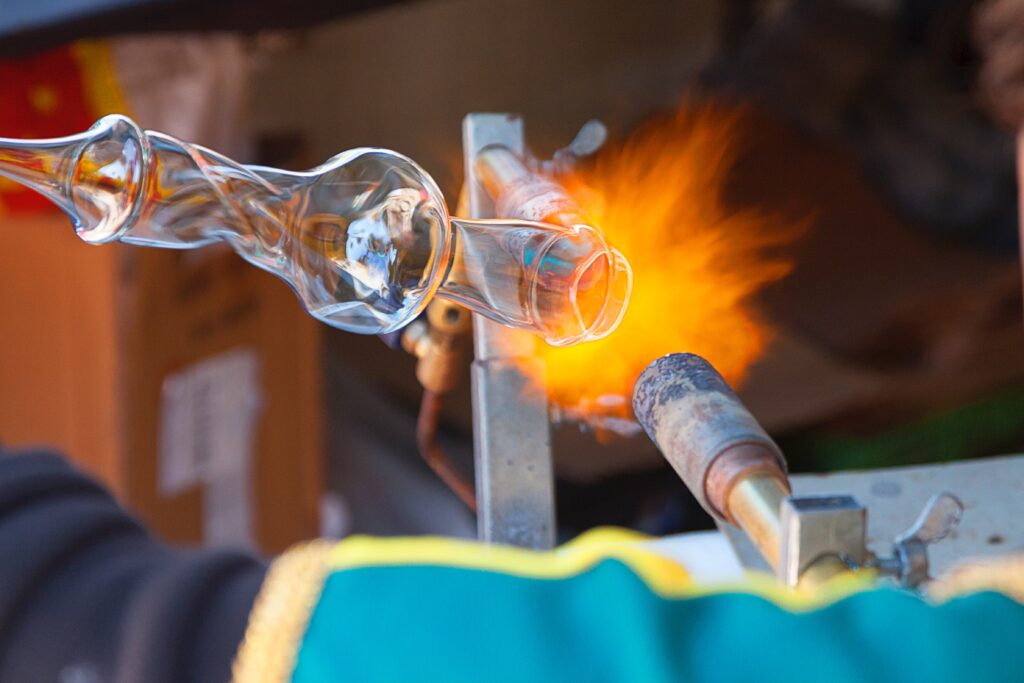
From the windows in skyscrapers to the screen on your smartphone, glass is one of the most versatile and essential materials in modern society. Known for its transparency, strength, and recyclability, glass plays a vital role in architecture, technology, art, and everyday life.
Whether you’re admiring a stained-glass window or drinking from a glass cup, this remarkable material combines beauty, function, and sustainability in countless ways.
What Is Glass?
Glass is a non-crystalline, amorphous solid typically made from silica (sand), soda ash, and limestone, heated to high temperatures and rapidly cooled. This process gives glass its unique transparency and hardness while allowing it to be molded into nearly any shape.
There are many types of glass, each designed for specific applications:
- Soda-lime glass – used in bottles, jars, and windows.
- Tempered glass – stronger and safer, ideal for car windows and shower doors.
- Borosilicate glass – resistant to heat and chemicals, used in laboratory glassware and cookware.
- Laminated glass – made by bonding layers for safety, used in architecture and vehicles.
How Is Glass Made?
The glass-making process combines art, science, and precision engineering:
- Raw materials (sand, soda ash, limestone) are mixed.
- The mixture is melted at around 1,700°C (3,092°F) in a furnace.
- The molten glass is formed into sheets, bottles, fibers, or other shapes.
- It is cooled and annealed slowly to remove internal stress.
This process can vary depending on the type and purpose of the glass.
Uses of Glass in Modern Life
Architecture and Construction
Glass brings natural light and modern aesthetics to buildings. From skyscraper facades to eco-friendly homes, glass contributes to energy efficiency and design innovation.
Automotive and Aerospace
Tempered and laminated glass ensures safety and visibility in vehicles and aircraft.
Technology and Electronics
Modern devices rely on smart glass, fiber optics, and touchscreen glass for connectivity and interactivity.
Art and Design
From stained glass windows to hand-blown sculptures, glass has been used as an art form for centuries.
Everyday Products
Glass bottles, jars, mirrors, and eyeglasses are just a few examples of its practical uses.
Environmental Benefits of Glass
One of the best things about glass is its sustainability:
- 100% recyclable without losing quality.
- Reduces waste and energy consumption.
- Plays a key role in green building and renewable energy (like solar panels).
Using recycled glass (called cullet) in production lowers the need for raw materials and reduces CO₂ emissions.
The Future of Glass
Innovations in glass technology are transforming industries:
- Smart glass that changes opacity for privacy or energy efficiency.
- Self-cleaning glass that uses nanotechnology.
- Ultra-thin flexible glass used in foldable screens.
- Solar glass that converts sunlight into energy.
As sustainability and design continue to evolve, glass will remain at the heart of innovation.
Why Glass Matters
Glass is more than just a transparent material it’s a symbol of progress, creativity, and sustainability. Its strength, recyclability, and endless versatility make it one of the world’s most valuable materials.
From ancient craftsmanship to futuristic smart glass, this material continues to shape how we live, build, and connect.
ALSO SEE : 10 Fascinating Facts About Rainwater You Probably Didn’t Know