Cement is one of the most essential materials in modern construction. From skyscrapers and bridges to houses and roads, cement plays a critical role in shaping infrastructure worldwide. Understanding how cement is made helps explain why it is so durable and widely used.
Raw Materials Used in Cement Production
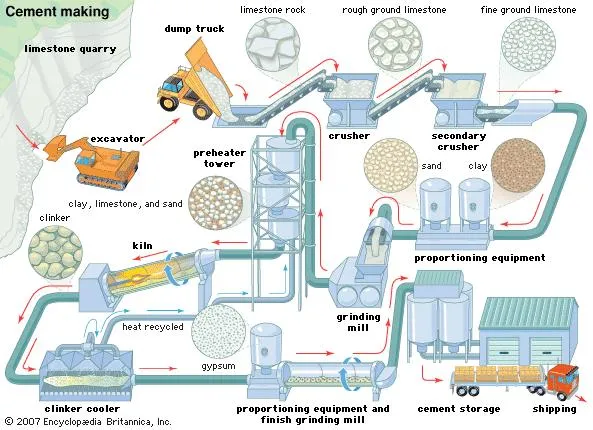
The primary raw materials used in cement manufacturing include limestone, clay, shale, and iron ore. Limestone provides calcium, while clay supplies silica, alumina, and iron. These materials are carefully selected and tested for quality.
Crushing and Grinding Process
The raw materials are crushed into small pieces and then ground into a fine powder known as raw meal. This process ensures uniform composition and efficient chemical reactions during heating.
Heating in the Rotary Kiln
The raw meal is fed into a rotary kiln, a large cylindrical furnace that rotates continuously. Inside the kiln, temperatures reach up to 1450 degrees Celsius. At this stage, chemical reactions transform the raw meal into clinker.
Clinker Cooling and Grinding
After leaving the kiln, the hot clinker is rapidly cooled to preserve its chemical properties. The cooled clinker is then ground with gypsum to produce fine cement powder.
Packaging and Distribution
The finished cement is stored in silos before being packed into bags or transported in bulk. It is then distributed to construction sites and retailers worldwide.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cement production contributes significantly to carbon emissions. To reduce environmental impact, manufacturers are adopting alternative fuels, improving energy efficiency, and developing eco friendly cement solutions.
Cement manufacturing is a complex but fascinating process that combines science, engineering, and technology. As the demand for sustainable construction grows, the cement industry continues to innovate for a greener future.